
This can help reduce the size of the defect to be covered.
#3 compartments of leg skin
Careful use of elastic retention sutures (elastic vessel loop woven through skin staples) can help counteract skin contraction, and be tightened progressively as swelling resolves. This is only permissible if it can be achieved without any skin tension it is inadvisable in smokers, who have impaired capacity for soft-tissue healing.įasciotomy wound edges tend to retract and become difficult to close.

It is tempting to the surgeon to try early secondary skin suture, rather than skin-graft coverage, once the swelling has subsided. 4 Identify the bones, ligaments, and cartilages of the knee and. 3 Identify the muscles, nerves, and vessels on the dorsum of the foot. 2 Identify the muscles in the anterior and lateral compartments of the leg and discuss their actions, innervations, and blood supply. The simplest and safest technique is to cover the healthy soft-tissue defect with a split skin graft: at a later date, when the limb contours have returned to normal, the grafted area can be excised and secondary skin closure performed without tension. 1 Identify bony features associated with the knee, leg, and ankle. Once any skeletal injury is under control, the fasciotomy wound(s) healthy and the swelling of the soft tissues has sufficiently regressed, consideration must be given to achieving skin coverage. Reperfusion injury is another cause of compartment syndrome. After blood flow is restored, capillaries leak and ischemic muscle swells.

This critical level is the tissue pressure which collapses the capillary bed and prevents low-pressure blood flow through the capillaries and into the venous drainage. Compartment syndrome occurs when the pressure within a closed osteo-fascial muscle compartment rises above a critical level.Compartment syndrome: the importance of early diagnosis. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics, 21(5), 680-688 Acute compartment syndrome in children: Contemporary diagnosis, treatment, and outcome. You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our editorial policy. We link primary sources - including studies, scientific references, and statistics - within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. Medical News Today has strict sourcing guidelines and draws only from peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical journals and associations. as the cells die, the muscle can release various chemicals that can damage the kidneys.
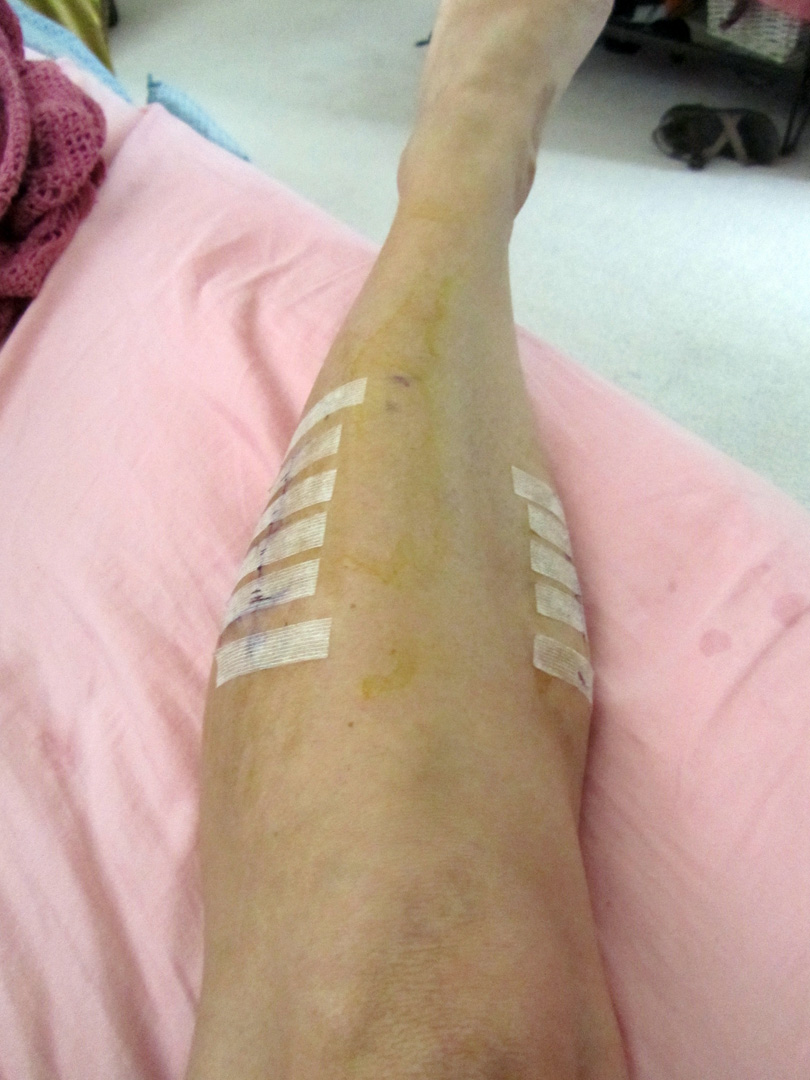
fasciotomy may cause permanent scarring.permanent muscle damage and reduced function in the affected limb.In some cases, acute compartment syndrome and its treatment can lead to:
#3 compartments of leg full
This may help to restore a full range of motion and muscle strength. If surgery is undertaken, some people may need a course of physiotherapy to help with the recovery process. Here, a doctor makes a cut in the fascia to give the muscles room to swell. Surgery is also an option if all other treatments have failed. People may also be advised to avoid the activity causing the problem. Options to treat chronic compartment syndrome include physiotherapy, shoe inserts, and anti-inflammatory medications. The procedure, called a fasciotomy, involves a surgeon cutting open the skin and the fascia to relieve the pressure. The only option to treat acute compartment syndrome is surgery. Share on Pinterest If compartment syndrome is suspected, patients should be directed to the emergency room.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
